Redux 基础概念
1. 安装依赖
2. 安装 Chrome 调试插件
const store = createStore(
reducer,
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__ && window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION__()
);3. createStore 源码
function createStore (reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) {
let currentReducer = reducer // 存放 reducer
let currentState = preloadedState // 闭包,存放 state
let currentListeners = []
let nextListeners = currentListeners // 存放所有的 listener
let isDispatching = false
function getState () {
return currentState // 返回闭包中 state 的结果
}
function subscribe (listener) {
nextListeners.push(listener) // 新增 listener
return function unsubscribe () {
const index = nextListeners.indexOf(listener)
nextListeners.splice(index, 1) // 移除 listener
}
}
function dispatch (action) {
if (isDispatching) {
// 防止在 reducer 中再次执行 dispatch
throw new Error('Reducers may not dispatch actions.')
}
try {
// 执行 dispatch 时,dispatch 为 true
// 相当于锁住了该状态,比如,防止在 reducer 中再次执行 dispatch
isDispatching = true
// 将闭包的 state, 和 action 进行计算,从而更新 state
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action)
} finally {
isDispatching = false
}
// 在 dispatch 之后,通知所有的 listener
const listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners)
for (let i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
const listener = listeners[i]
listener()
}
return action
}
dispatch({ type: `@@redux/INIT+随机数` })
return {
dispatch,
subscribe,
getState
}
}4. 简单示例
5. 什么是 Action Creator
6. Reducer
6.1 reducer必须是纯函数
7. Reducer 的拆分
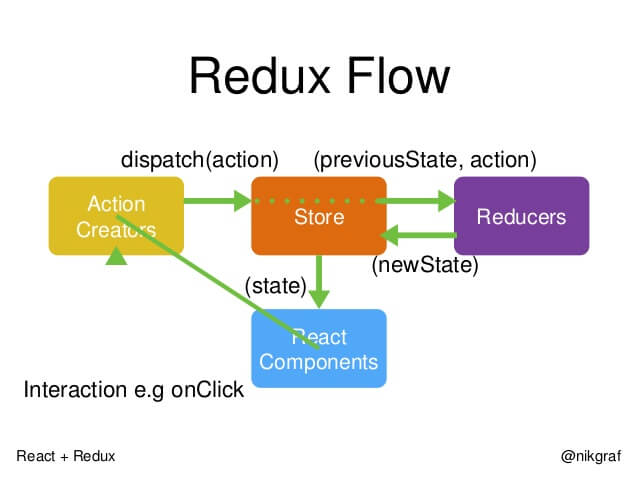
8. 工作流程梳理
参考文档
Last updated